What is Validation in Design Thinking?
- Definition: Validation is the process of testing and confirming that design solutions effectively address users’ needs and expectations.
- Objective: The goal is to prevent costly errors and ensure that the final solution genuinely solves the intended problem.
- Ongoing Process: Rather than being a one-off task, validation should be a continuous activity spread throughout the design process.

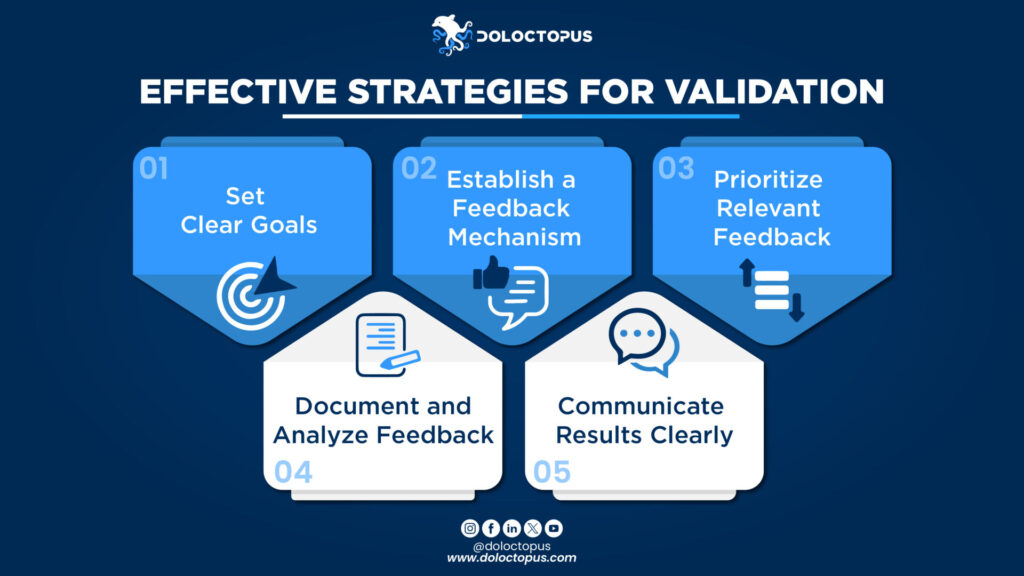
Effective Strategies for Validation
-
Set Clear Goals
- Clearly define what you aim to achieve with the validation process.
- Focus on specific elements of the solution that would require further testing.
-
Establish a Feedback Mechanism
- Create a structured system for receiving and incorporating user feedback.
- Use tools like surveys, interviews, and usability tests to continuously collect input.
-
Prioritize Relevant Feedback
- Evaluate feedback based on its importance and impact.
- Address feedback that highlights critical issues or offers significant insights.
-
Document and Analyze Feedback
- Keep thorough records of all feedback and findings.
- Analyze this data to spot trends and areas needing tweaks.
-
Communicate Results Clearly
- Share insights and recommendations with the team and stakeholders in a clear and actionable format.
- Ensure that everyone involved is up-to-date and aligned on the next steps.
Key Best Practices for Validation
-
Conduct Testing Early and Regularly
- Begin testing ideas preferably at the earliest stage of the process, to gather feedback before committing significant resources.
- Listen properly to feedback, and repeat testing throughout the development to refine and improve the solution in parallel to that.
-
Involve Actual Users
- Engage with real users who match your target demographic to obtain genuine feedback.
- This real-world input helps uncover actual user experiences, preferences, and challenges.
-
Utilize Prototypes
- Develop prototypes that can range from basic sketches to sophisticated interactive models.
- Prototypes are crucial for collecting actionable feedback and making iterative improvements.
-
Collect Both Qualitative and Quantitative Feedback
- Gather qualitative insights to understand user experiences and feelings.
- Collect quantitative data to measure trends and metrics.
- Integrating both types of feedback provides a comprehensive view of how the solution performs.
-
Iterate Based on User Feedback
- Review and analyze feedback to make necessary changes and retest.
- Iteration helps in progressively refining the solution to meet user needs better.
Validation is a very crucial component of design thinking, which ensures innovative and practical solutions throughout the process. By following these guidelines, design teams can enhance their solutions, mitigate risks, and deliver impactful outcomes, just like that!


